Hemoglobin A1C — What is It?
Author : Christine Gallup, MS, RD, LDNA hemoglobin A1C (aka glycated hemoglobin) test gives a picture of a person’s average blood sugar over the previous two to three months. This helps give practitioners a better idea of a person’s overall blood sugar management rather than focusing on one day or one blood test.
Hemoglobin is found inside red blood cells. Because hemoglobin is made up of protein, it likes to link up with sugar. To put it simply, the more sugar that is found in a person’s blood, the more that will be found in the hemoglobin.
A1C is the “memory” that red blood cells have of blood sugar levels. For example, if a person’s blood sugars were high last week, but are fine this week, the red blood cells will still “remember” the high sugars from last week. Our red blood cells continue to remember for approximately 120 days — this is why a hemoglobin A1C test indicates how someone’s blood sugars have been for the past two to three months.
A1C tests cannot replace daily blood sugar checks. It is another tool to use to help confirm self-testing results, give treatment plan feedback and show how healthy choices can make a difference.
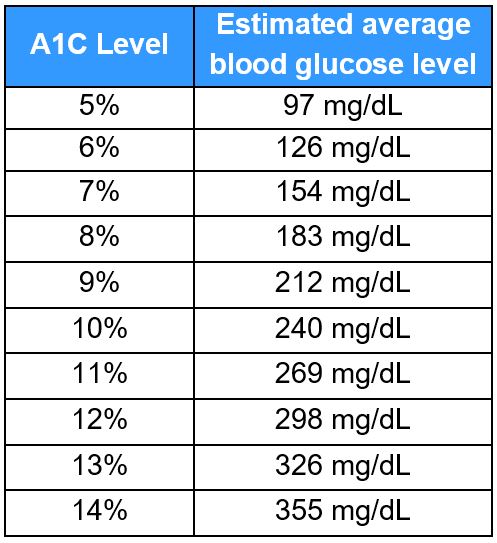
The target range for a hemoglobin A1C is less than 7%. Here’s how an A1C level corresponds to average blood sugar levels:
If patients are struggling with high A1C levels, follow-up with an endocrinologist and registered dietitian is critical in order to achieve better results. Blood sugars that are within a reasonable range will help prevent further loss of kidney function and help patients feel better overall, resulting in an improved quality of life.